数学知识
约数(因数)个数
- 因数总是成对出现的,一个在开根号左边,一个在右边,此时因数个数加二
- 特殊情况:有可能刚好等于开根号之后的数字,此时因数个数只加一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n,a[N];
int main(){
cin >> n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int cnt=0;
for(int j=1;j*j<=a[i];j++){
if(a[i] % j == 0 && j*j != a[i]) cnt+=2;
if(a[i] % j == 0 && j*j == a[i]) cnt+=1;
}
cout << cnt << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
|
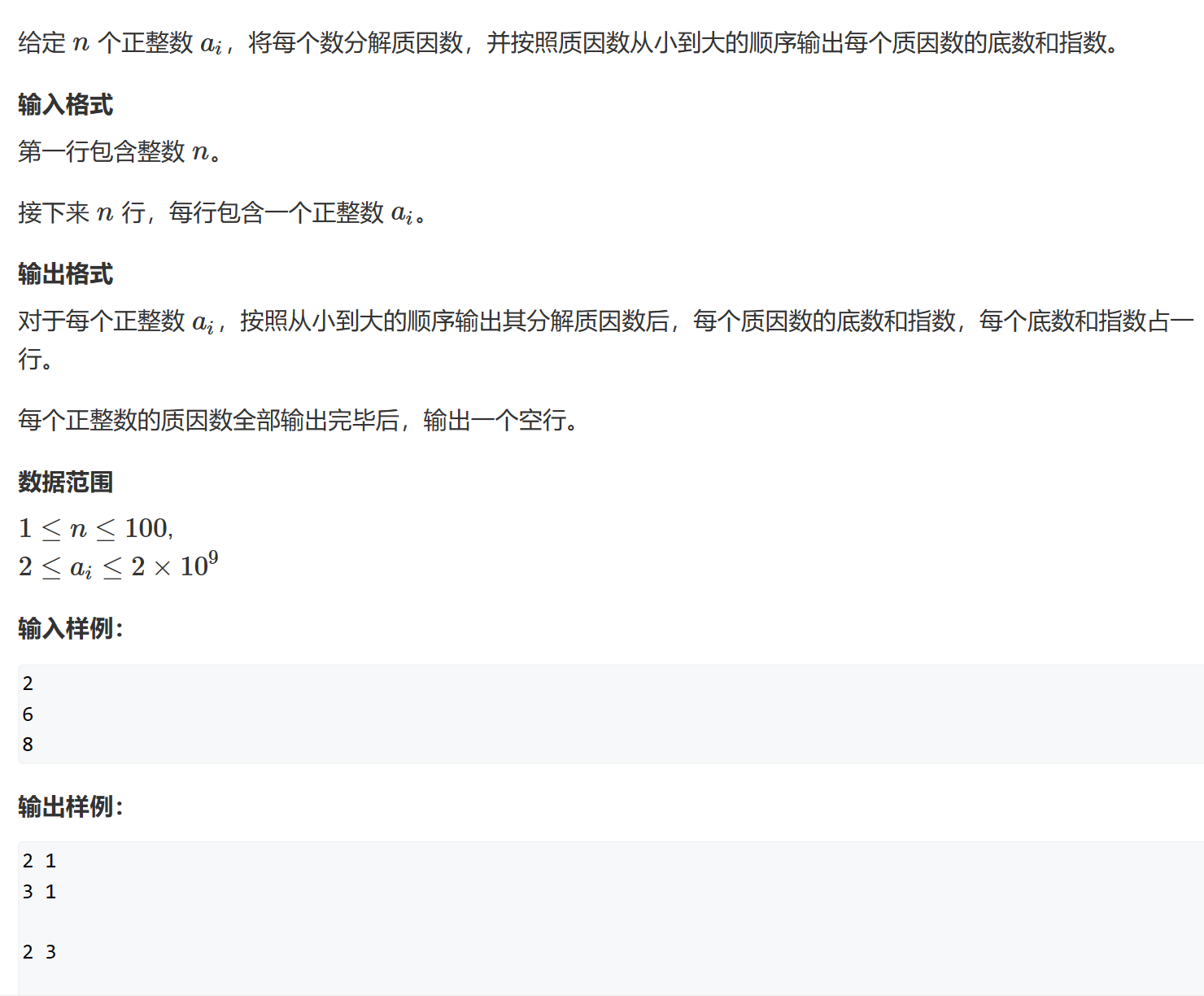
分解质因数
题目链接:分解质因数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n,a[N];
int main(){
cin >> n;
while(n--){
int x;
cin >> x;
int m = x;
for(int i=2;i*i<=x;i++){
if(x%i == 0){
int cnt = 0;
while(x%i == 0){
x /= i;
cnt++;
}
cout << i << " " << cnt << "\n";
}
}
if(x > 1) cout << x << " 1" << "\n";
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
|
欧几里得算法
$ gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, a mod b) $
欧拉函数
互质数:
两个数的公因数只有1的两个非零自然数,叫做互质数
1与任何数都互斥,自身与自身不互斥(公约数包括1和自身)
性质一:两个不同的质数是互质的。
性质二:一个质数,另一个不为它的倍数,这两个数为互质数。(较大数是质数的两个数是互质数)
性质三:相邻的两个自然数是互质数。
性质四:相邻的两个奇数是互质数。
性质五:最大公约数是1,两个数互质。
欧拉函数
定义:对于一个正整数n,n的欧拉函数ϕ(n)表示小于等于n中,与n互质的正整数的个数
分解质因数:N = $ p_1^{a_1} * p_2^{a_2} * …*p_n^{a_n} $
$ ϕ(N) = N(1- \frac{1}{p_1})(1- \frac{1}{p_2})…(1- \frac{1}{p_n}) $
用代码表示该公式时为了防止出现小数,用以下方式表示:
$ ϕ(N) = (\frac{N}{p_1})*(p_1 - 1) $
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| for(int i=2;i<=t/i;i++){
if(t%i == 0){
res = (res/i)*(i-1);
while(t%i == 0){
t /= i;
}
}
}
if(t > 1) res = (res/t)*(t-1);
cout << res << endl;
|
性质1:如果n是质数,那么ϕ(n) = n−1,因为只有n本身与它不互质。
性质2:如果p,q都是质数,那么$ ϕ ( p ∗ q ) = ϕ ( p ) ∗ ϕ ( q ) = ( p − 1 ) ∗ ( q − 1 ) $.
快速幂
快速幂,二进制取幂,在O(logn)下求$ a^n $的方法
求 $ {a^b} % {p} $ 的值
做这个题前首先我们需要了解一下关于取余的公式
(a + b) % p = (a % p + b % p) % p
(a - b) % p = (a % p - b % p ) % p
(a * b) % p = (a % p * b % p) % p
$ a^b = a^{2^0+2^1+…+2^n(中的某几项)} $
ex. $ a^{10} = a^{(1010)_2} = a^{2^1+2^3} $
注意下述式子
$ a^{2^3} = (a^{2^2})^2 \ a^{2^0} = a $
第二个式子即可解释代码中的 a = a*a % p;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| #include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL a,b;
int p,n;
int main(){
cin >> n;
while(n--){
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&p);
LL res = 1;
while(b > 0){
if(b & 1){
res = res * a % p;
}
a = a*a % p;
b = b >> 1;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
矩阵快速幂
矩阵快速幂算法详细解析

矩阵快速幂主要是解决n很大的递推式问题
ex. f(n)=4f(n-1)+3f(n-2)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| #include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
long long int m[10][10];
}ans,res;
node mul(node A,node B)
{
int i,j,k;
node temp;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<n; j++)
{
temp.m[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<n; j++)
{
for(k=0; k<n; k++)
{
temp.m[i][j] += (A.m[i][k] * B.m[k][j])%666666;
}
}
}
return temp;
}
node quickpower(node a,long long n)
{
node c;
memset(c.m,0,sizeof(c.m));
int i;
for(i=0;i<2;i++) c.m[i][i]=1;
while(n)
{
if(n & 1)
{
c=mul(c,a);
}
a=mul(a,a);
n=n>>1;
}
return c;
}
int main()
{
long long n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
memset(ans.m,0,sizeof(ans.m));
ans.m[0][0]=4;
ans.m[0][1]=3;
ans.m[1][0]=1;
ans.m[1][1]=0;
n=n-2;
ans=quickpower(ans,n);
memset(res.m,0,sizeof(res.m));
res.m[0][0]=233;
res.m[1][0]=4;
res=mul(ans,res);
k=k-res.m[0][0];
cout<<k<<endl;
return 0;
}
|

